How-to Initiate a Project
When starting a new project there are several tasks to be performed to ensure that tools and systems are well set up when M0/G0, M1/G1, and M2/G2 are reached.
This guide describes these tasks and has three main sections with multiple activities under each:

Brief descriptions of many artifacts and plans referred to in this guide are available under Details, while links to templates for milestone tracker checklists and gate presentations are listed under References.
Prerequisites
To be able to initiate a project within PCP R&D, the following needs to be ready by M0/G0:
- Market opportunities (MOs) from Portfolio and Product Management (PPM).
- Draft of system requirements from PPM.
- Development Overview Statement (DOS) from PPM.
- The project must be aligned with PCP R&D’s vision and roadmap presented in increment vision.
In addition, it can be valuable to have a look at the list of Good Practices with relevant experiences from earlier projects.
Note Safety projects require additional artifacts and activities according to the Safety Handbook and 3BSE039313 Names on RACI.
Intended for
Release owners, configuration managers, product managers, quality control managers, cyber security engineers, and test leads.
Other roles outside of PCP R&D, such as cross-functional team leads and gate assessors, may also benefit from the content in this guide.
G0-related activities
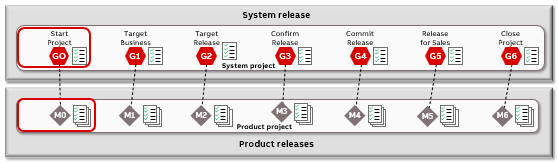
Identify release type
Release owner, stream owner, and product manager identify the most suitable release type for the release. See Release Types for further information regarding release categories and types. Document the decision of release type in the first gate or milestone presentation.
Identify key roles & SteCo
Release owner makes a draft for key roles and steering committee (SteCo) for the release, which is needed to have a decision forum at M0/G0. Key roles include gate/milestone owner, gate assessor (for gated releases), quality control manager, and configuration manager. The SteCo usually includes release owner, stream owner, and managers on different levels depending on release type. Consult with the stream lead to identify suitable individuals for the SteCo. For more information about SteCo governance and SteCo meetings, see Maintain SteCo & Governance.
Identify representatives for applicable cross-functions (drivers and accountable) within PCP:
- Business Process & Information Systems (including price book management, sales configuration management, and license management)
- Industrial Engineering
- L3 Support
- Sales Enablement & Marcom
- Planning & Fulfillment (P&F)
- PPM
- Procurement & Logistics (P&L)
- Supply Quality Management
Handshake above roles with stream lead or corresponding organizational roles.
Prepare documentation structures
It is recommended to prepare DMS and Teams before G0 to establish a good structure for the required G0 documentation. Preparing the documentation structures at this stage helps to prevent extra work further ahead.
Discuss and prepare the following together with the configuration manager:
- Project folder structure in DMS (needed for e.g. G0 checklist).
- Project folder structure and access rights in MS Teams.
- Allocation of project document ID (to use with sub-numbers) in the document control plan (DCP). Use the ABB Identity Number Generator to create document IDs.
Set preliminary scope and plan
Work together with PPM to identify high-level scope based on market opportunities. It is important to ensure that there are resources and budget for G0-G1 activities, and that the proposed time plan is realistic.
Prepare budget in NORRD
Establish project and work packages in NORRD.
Perform cross-functional pre-M0/G0
Set up meetings with relevant PCP cross-functions to identify deliverables and activities, and to establish plans. Update, review, and approve the applicable cross-functional milestone trackers, and prepare input to the gate/milestone meeting.
Initial kick-off meeting
If a longer pre-study phase is required as a part of the project, a separate kick-off meeting can be held before the M0/G0 meeting. Involve the affected functions in the kick-off meeting and align on the initial vision, objectives and high-level plan.
M0/G0 meeting
Establish checklists and gate/milestone presentation according to Gate Model & Milestone Checklists, where links to templates also are available.
Perform gate assessment (for gated projects).
Conduct M0/G0 meeting including decision (Go / Go with action item / Redo / Terminate) and document all actions with due dates.
G1-related activities
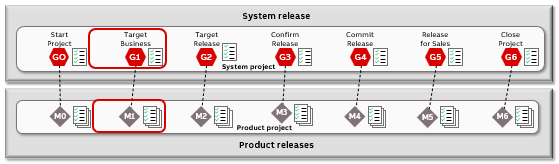
Prepare tools and systems
If not already done, set up DMS and MS Teams according to Prepare documentation structures.
Establish structures for strictly confidential documentation, e.g. relating to intellectual property and cyber security.
Ensure that configuration management (CM) sets up a project in Azure DevOps (ADO), including:
- Access rights in ADO.
- ADO query structure – shared queries.
- ADO team setup (if applicable).
- Area and iteration paths.
Ensure that the product manager adds the release object to Decision Focus, where all requirements will be allocated.
Set high-level scope
Collaborate with PPM to:
- Ensure approval of system requirements before M1/G1 meeting, see System Requirement Review Guideline.
- Refine functional system epics based on system requirements in Decision Focus.
- Add potential enablers / architectural system epics.
Ensure that the product owner, architects, and technical experts make a first estimate whether the given timeframe and resources are realistic. If needed, request scope discussion / negotiations with PPM.
Establish project organization
Identify needed resources for work to be done between G1 and G2, both within R&D and other PCP organizations. Keep in mind that a system requirement may affect multiple streams.
Prepare plans
Initiate drafts of all plans according to RACI:
- Project description and plan (PDP).
- Names on RACI.
- Organization chart.
- Project schedule.
- Configuration management plan.
- Quality plan, including KPIs.
- Document control plan (DCP).
- User documentation control plan (if not included in DCP).
- Test strategy and plan.
- Integration plan.
- Risk list.
Initiate technical work
Analyze system epics and architectural matters to get an overall technical understanding of the release, its complexity, and its impact on streams and products.
Identify work packages and their initial estimates.
Decide if a proof-of-concept phase (for software and/or hardware) is needed before M2/G2 as an early-stage development to verify the design concept.
Intellectual property
Prepare an IP risk register.
In collaboration with the IP officer, analyse the IP risk register, and if it is identified that the project may lead to a substantial advance in a technological field, a business of strategic and economic relevance, or a field with particularly challenging competition, the project will be identified as an IP key project. Further information is available in 7PAA009006 IP in Projects.
For IP key projects the IP process is more complex, and the following is required:
- Establishment of an IP core team (involving a patent attorney assigned to the project).
- Establishment of an IP strategy report.
- Issuance of an IP risk analysis report by ABB’s intellectual property service organization (IPSO) by M2/G2.
3rd-party software and OSS
Create a project in BlackDuck Hub.
Quality audit
The quality control manager performs a quality audit, which results in a quality report.
Perform cross-functional pre-M1/G1
Set up meetings with relevant PCP cross-functions to identify deliverables and activities, and to establish plans. Update, review, and approve the applicable cross-functional milestone trackers, and prepare input to the gate/milestone meeting.
M1/G1 meeting
Confirm governance and release type.
Establish/update checklists and gate/milestone presentation according to Gate Model & Milestone Checklists, where links to templates also are available.
Perform gate assessment (for gated projects).
Conduct M1/G1 meeting including decision (Go\Go with action item\Redo\Terminate) and document all actions with due dates.
G2-related activities
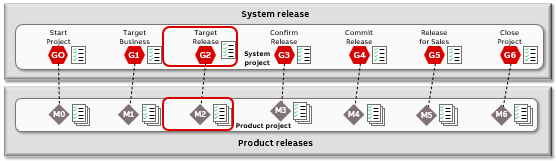
Confirm scope
System epics must be approved, and epics must be agreed before M2/G2, see How-to Work with Epics and Features for further information. In addition, R&D-internal architecture/enabler epics shall be considered (e.g. architectural evaluations, IP-related work items, and refactoring).
Initiate planning and definition of features before M2/G2 to enable an efficient start of the development work. Consider priorities and dependencies, within and between streams.
Identify training needs
Identify any training needs, e.g. related to Functional Safety or Cyber Security, together with line management.
Finalize plans
Finalize, review and approve all plans:
- Project description and plan (PDP).
- Names on RACI.
- Organization chart.
- Project schedule.
- Configuration management plan.
- Quality plan, including KPIs.
- Document control plan (DCP).
- User documentation control plan (if not included in DCP).
- Test strategy and plan.
- Integration plan.
- Risk list.
Prepare tests
Apart from finalizing test strategy and plan, sync with the test team to e.g.:
- Plan and establish test environment and set-up.
- Identify potential new equipment needs.
- Draft the detailed test plan, including plans for pre-DSAC and DSAC.
If division testing is required, set up plans in collaboration with the actual divisions on library impact and adaptations, delivery dates of updated libraries, software, hardware, test plan (tests executed by division, or internally in PCP), test scope, and test schedule.
3rd-party software and OSS
Identify potential new 3rd-party suppliers to be qualified according to the 3rd Party Software Qualification Process Description.
Execute a BlackDuck scanning. Identify license and operational risks and plan for patch management.
Perform a risk analysis of security and operational risks according to How-to Handle Vulnerabilities in 3rd-party Software and How-to-Handle 3rd-Party Software EoL.
Establish a 3rd-party components list and shared query in Decision Focus in collaboration with the 3rd-party software manager.
Export control
Request access to export control-related documentation from the trade compliance officer (TCO).
Define strategy on how to handle export control in collaboration with the TCO, e.g. if a full export control classification is required.
Create a draft for the “Product Classification input Data” document (for new products) or “Decision Flow” document (for existing products). Identify any constraints in terms of dual-use classification, US-content, and cryptography content, which results in a need for a full classification.
Sync with the TCO on any identified constraints in terms of dual-use classification, US-content, and cryptography content (in ABB-developed software and 3rd-party software). In case of constraints, define mitigations for internal development distribution, beta site distribution, and release distribution.
Prepare development environment
Establish development environment in collaboration with the configuration manager:
- Prepare document baselines (if applicable).
- Prepare code environment in ADO, including code base, build environment, pipelines, and version control system.
- Prepare for architectural work, e.g. decide architecture tooling and techniques, branch out enterprise architect model, handling of Git repos, etc.
- Define static code analysis tool(s), rule sets, and how to handle results.
Note: There is a big difference in effort depending on project type and size, which impacts how much can be copied from earlier projects.
Intellectual property
The following should be addressed together with the project’s IP officer:
- Updated IP risk register, including mitigation of IP risks.
- If identified as required, prepare an IP strategy report.
- If identified as required, prepare a 3rd-party IP risk analysis (needs to be done by a patent attorney).
- Perform potential actions from the above according to the IP process.
Cyber security
The following activities should be performed before M2/G2:
- Initial cyber security assessment report to identify gaps to be completed before G5, see Cyber Security Assessment for further details. Create work items for the gaps.
- Planning of additional security testing according to the Security Testing Guideline.
- Initiation of open-source software scanning activities.
- Check Black Duck status for security risks.
- Draft of security architecture, including security context.
- Draft of security criticality analysis and attack surface analysis.
- Draft of threat model.
Quality control and audit
Establish dashboards (in TFS/ADO, Power-BI, etc.) according to KPIs defined in the quality plan.
The quality control manager performs a quality audit, which results in a quality report.
Perform cross-functional pre-M2/G2
Set up meetings with relevant PCP cross-functions to identify deliverables and activities, and to establish plans. Update, review, and approve the applicable cross-functional milestone trackers, and prepare input to the Milestone/Gate meeting.
M2/G2 meeting
Establish/update checklists and gate/milestone presentation according to Gate Model & Milestone Checklists, where links to templates also are available.
Perform gate assessment (for gated projects).
Conduct M2/G2 meeting including decision (Go / Go with action item / Redo / Terminate) and document all actions with due dates.
Details
Below paragraphs give brief explanations of plans, artifacts, etc. included in this guide. Further details are available under the process area descriptions.
Configuration management plan
The configuration management (CM) plan describes how CM activities are performed within the project, e.g. identification and description of the overall CM policies and methods within the project, change control, and configuration identification and naming. The configuration manager is responsible for the CM plan.
Link to template: 7PAA001177F Configuration Management Plan
Cyber security assessment reports
Cyber security assessments are required for all releases. A number of cyber security assessment tools are available in the Cyber Security folder in Templafy.
Product Classification Decision Flow
The Product Classification Decision Flow document contains a series of logical steps covering the most typical use cases of product change and provides a result which can be either “Full Classification” or “Light Classification”. If the result is “Full Classification” on at least one of the questions in the Decision Flow, then the existing product must be re-classified.
Link to template: 7PAA016324 Decision Flow
Product Classification Input Data
The Product Classification Input Data document collects all main information needed to perform the classification of the product, e.g. scope of changes, US-content, cryptography content, and 3rd party content. It covers both hardware and software. PM, with support from R&D and P&L, is responsible for the Product Classification input Data document.
Link to template: 7PAA016325 General Product Classification input Data
Division testing
Division testing (also known as enhanced testing) is an optional stage of testing that is carried out with divisions (e.g., PAEN, PAPI, PADI) if it is relevant to the respective product or system release.
Document control plan (DCP)
The DCP includes a list of all project and product related documentation created or updated in the project/release. This includes both documents stored in OnePCP DMS and markdown files in ADO along with information about document number in OnePCP DMS or location in ADO, revision, life cycle status, document owner and approver. The release owner is responsible for the document control plan.
Link to template: 7PAA007509 Document Control Plan
Integration plan
The integration plan includes information about when project artifacts (e.g. components and products) are integrated into a product or system baseline. The integration plan can be created in Excel (ref. template), MS project or directly in TFS/ADO. The release owner is responsible for the integration plan.
Link to template: 3BSE055542 System Integration Plan
IP risk register
The IP risk register is a document used to identify, evaluate and document the mitigation for IP risks that threaten the ability to deliver the R&D project objectives. The release owner is responsible for the IP risk register.
Link to template: 2PAA121471 IP Risk Register
IP strategy report
The IP strategy report helps to identify the key innovative and business-relevant aspects to focus IP protection efforts on and the type of IP assets likely to be required to deliver the project objectives. This report is only established if identified as needed by the IP officer. The release owner is responsible for the IP strategy report.
Link to template: 2PAA121473 IP Strategy Report
3rd-party IP risk analysis
The third-party IP risk analysis is a legal analysis of the risks from third-party IP that is used to evaluate or quantify uncertain risks and to recommend suitable mitigation. It may include a specialist patent search designed to support the objectives of the risk analysis.
The third-party IP risk analysis is only established if identified as needed by the IP Officer. It is strictly confidential and established and managed by a patent attorney/IP legal. The third-party IP risk analysis must only be distributed to a restricted circulation list (e.g. project lead, Division IP Officer).
Names on RACI
The responsible-accountable-consulted-informed (RACI) document includes information about which artifacts to create during a project/release. It shows the roles involved and when to create and approve the artifacts. The RACI is also used as a skeleton for "Names on RACI", where the actual names of persons who have the different roles are filled in. The release owner is responsible for the project’s RACI.
Link to template: 3BSE039313 Names on RACI
Organization chart
The organization chart gives a visual picture of the project organization including project team, streams- and product-organizations, cross-function teams, and SteCo. The organization chart can e.g. be created PowerPoint, Vision or Excel. The organization chart can be included in a separate tab in the Names on RACI document. The release owner is responsible for the organization chart.
Project description and plan
The PDP includes fundamental information about the project/release, e.g. background and objectives, scope, organization and roles, way of working, constraints and risks, schedule, and budget. The goal is not to keep all data updated in this plan but to provide links to all relevant documents and sources, e.g. in OnePCP DMS, Teams, TFS/ADO, and NORRD. The release owner is responsible for the PDP.
Link to template: 3BSE034121 Project Description and Plan
Project schedule
The time schedule includes information about when gates, milestones, beta versions, development activities, test activities, etc. are planned during the project/release timeline. The time schedule is typically created in Excel, MS Project, ADO, or PPT. The release owner is responsible for the project schedule.
Quality plan
The Quality plan is established in collaboration with the quality control manager (QCM) and describes how the QMS is applied with tailoring, quality KPIs, quality control and quality assurance.
Link to template: 7PAA003088 Quality Plan
Risk and opportunity list
The risk and opportunity list includes a list of all risks identified. This document shall be regularly reviewed and updated with new risks and changed status of existing risks. It also serves as a list of opportunities, i.e. items that possibly can turn out as an improvement in the project/release.
The risk list can either be kept in Excel (ref. template), or directly in TFS/ADO, which can be exported into a document (ref. the risk management process). The release owner is responsible for the risk and opportunity list.
Link to template: 7PAA012026 Risk List
Test strategy and plan
The test strategy and plan includes information about the test strategy for the product, stream and/or system. It describes how system requirements (system epics and epics) are tested, in which test levels, test stages, test environments, etc. The test lead is responsible for the test strategy and plan.
Link to template: 7PAA015399 Test Strategy and Plan
User documentation control plan
The user documentation control plan includes a list of all user instructions created or updated in the project, such as installation guides, configuration guides, operation guides, system guides, and release notes. For all documents listed, it also includes information about document number in DMS or location in ADO, revision, life cycle status, document owner and approver.
The user document can be included in the DCP (in a separate tab), or as a separate document. The release owner is responsible for the user documentation control plan.
Link to template: 7PAA007509 Document Control Plan
References
- 3rd Party Software Qualification Process Description
- 7PAA009006 IP in Projects
- Gate Model & Milestone Checklists
- Good Practices
- How-to-Handle 3rd-Party Software EoL
- How-to Handle Vulnerabilities in 3rd-party Software
- How-to Work with Epics and Features
- PMO share point area
- Product & Portfolio Management process
- Product classification
- Project Governance and Performance
- Release Types
- Risk management process
- Safety Handbook
- Security Testing Guideline
- System Requirement Review Guideline